Semantic search is a new way of finding information that looks at the meaning and purpose of what you ask, rather than just matching words like older methods do. In today’s world full of information, people want searches that are smarter, quicker, and more relevant.
Unlike regular search engines that only find exact word matches, semantic search uses tools like NLP, machine learning, and vector embeddings. These tools help it understand the meaning, connections, and details in the data.
This helps the system provide better answers, even if the user’s question is unclear, worded differently, or not fully detailed. Semantic search makes it easier for people to find the right product in an online store or get answers to difficult questions.
It shows a big progress in making searches easier, more natural, and better. As technology changes, semantic search is important for making user experiences more useful and personal, and we will see in detail about it in this post.
What is Semantic Search?
Semantic search is a way that search engines look at the meaning of a question to give better answers. It uses AI tools like ML, and NLP and machine learning to understand what words mean and what someone is looking for when they search.
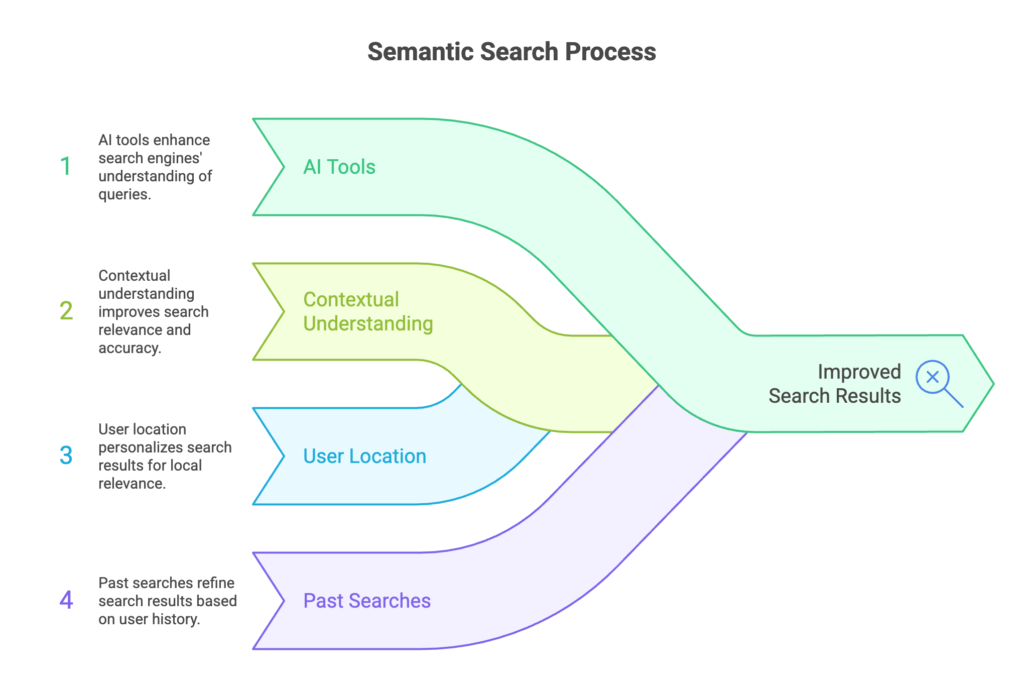
It goes beyond regular search tools that look for exact keyword matches. Instead, a semantic search engine looks at things like:
- Connections between the words in the search query
- The place where the person searching is located, especially for searches that show local results
- Past searches that give a better understanding of the meaning in context
The result is the information that matches what the user is looking for and helps them find what they need.
How Does Keyword Search Differ From Semantic Search?
A keyword search looks for specific words in databases or documents without considering what those words really mean. Also known as word search or text search, it’s an easier method that is quicker to set up, but it often gives results that are not very relevant.
Semantic search looks at the meaning and purpose behind what a user is searching for, not just the specific words they use. It uses a method called vector search to find similarities and connections. This makes searches more conversational and usually leads to better search results.
Is Google Considered as a Semantic Search Engine?
Google is one of several search engines that uses semantic understanding. Over time, Google has changed from regular search results to a smarter search that understands the meaning behind words.
In 2012, Google introduced the Knowledge Graph, which is a database that contains information about people, places, and things.
In 2013, Google made a big change called Hummingbird. Instead of just matching words, it focused on understanding the topics by using more natural language.
In 2015, Google introduced RankBrain, its first system using artificial intelligence and deep learning. This system helps the search engine understand how words relate to ideas, making it easier to find relevant information.
In 2018, BERT was a new way to prepare language for computers. It helped search engines understand complicated, conversational questions better and give more accurate answers.
In 2021, MUM, an AI tool, helps Google do more than just find information. It can also create answers and responses.
Working of Semantic Search
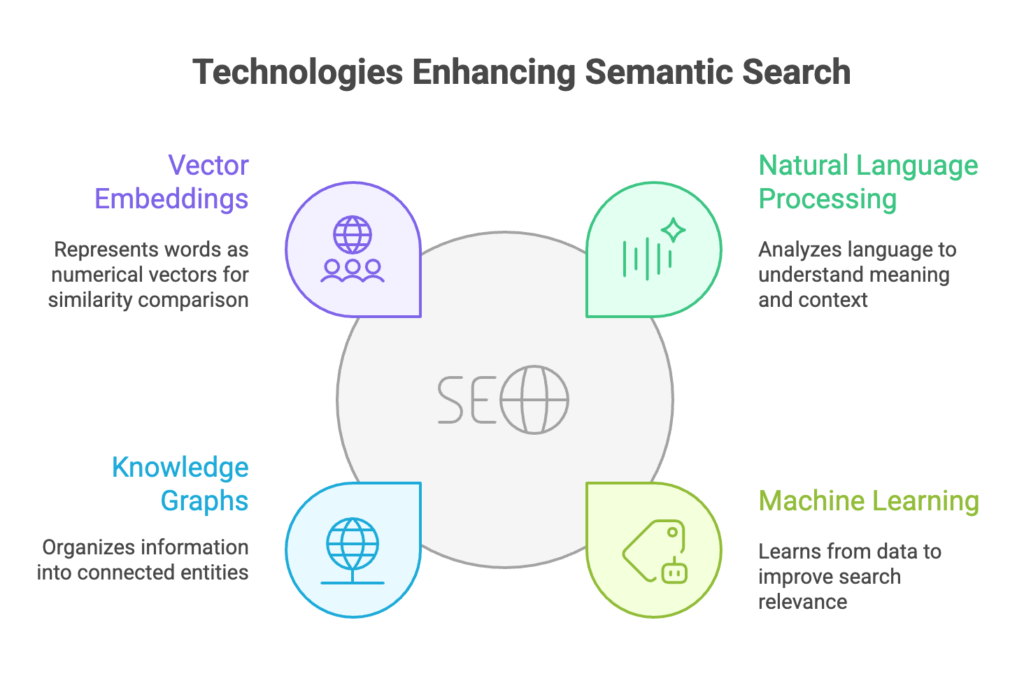
Semantic search uses four main technologies to find and create information:
Natural Language Processing
NLP is the basis for understanding meaning in search. It helps machines interpret human language, getting the meaning even if they don’t just find the exact words. In semantic search, NLP techniques are used to analyze user questions and documents to find important details, connections, context, and feelings.
Methods like breaking text into smaller pieces, labeling words by their function, identifying names of people, and analyzing sentence structure help them understand the meaning and grammar of written text.
Advanced language models can understand words that mean the same thing, common phrases, and unclear sentences. This helps the system figure out what the user wants to say instead of just looking for specific words.
For example, if someone looks up “tallest building in the world,” NLP helps the system understand what that means and find information about the Burj Khalifa, even if those exact words aren’t used. So, NLP acts as a connection between human language and the way machines understand it in search systems.
Machine Learning
ML improves semantic search by finding patterns in large amounts of data. It keeps getting better at showing relevant search results based on how users act and their feedback. ML models can look at past search results, what users clicked on, and how they interacted with the data to figure out which results are the most helpful for different types of questions.
Supervised learning methods train models using labeled data to sort or rank documents by how similar they are to a question. Unsupervised learning, like grouping similar items or finding topics, can reveal patterns in data.
This helps to sort and find content more effectively. Reinforcement learning can be used to gradually improve how search results are ranked over time. Machine learning makes search smarter, making it more accurate and tailored to individual needs.
For example, if people often click on specific types of search results for a question, machine learning programs can learn to show those results first for future users. This helps give search results that are more relevant and related to what people want.
Knowledge Graphs
Knowledge graphs are important for semantic search because they help organize information into connected pieces and relationships, similar to how people understand context.
Unlike regular databases, knowledge graphs organize information like a network. They use points (called entities) and connections (called relationships) to show not just what things are but also how they are connected to one another.
For example, in a knowledge graph, “Einstein” might be connected to “Theory of Relativity,” “Germany,” and “Physicist”. When someone searches for “German physicist who developed relativity,” the system can understand and find that the answer is “Einstein”.
Knowledge graphs are created using both organized and unorganized information, and they use plans to keep everything consistent. They make it easier to understand different meanings, recognize items, and be aware of context in searches.
This leads to better and more relevant results. Knowledge graphs improve search results by connecting ideas, making it possible to find information based on concepts instead of just keywords.
Vector Embeddings
Vector embeddings are ways to represent words, phrases, or documents using numbers in a space where similar items are placed near each other. These are very important because they help the system compare how similar a query is to the content by using vector distance metrics such as cosine similarity.
Unlike keyword searches that look for exact words, embeddings understand the meaning and context of language. For example, the words “doctor” and “physician” will have similar meanings in a computer’s understanding, even though they are different words.
These special word representations are made using deep learning tools like Word2Vec, GloVe, BERT, or newer models that are transformer-based. By changing both the user’s question and the documents into numbers, the search engine can find the most relevant results even if the exact words don’t match.
Vector embeddings improve semantic search by making it stronger, able to grow larger, and better at understanding subtle meanings, context, and connections in data.
Why is Semantic Search Important?
Better Search Relevance
Overall, searches are getting more complex. At the 2024 Google Marketing Live Keynote, Philipp Schindler said that searches with five or more words have grown 1.5 times faster than shorter searches.
Semantic search makes search results more relevant by figuring out what users really mean and want, instead of just looking for specific words. Regular search engines usually give back results that match the exact words you typed, even if those results don’t make sense in the situation.
Semantic search understands what users are saying, recognizes important things, and looks at how different ideas are connected. For instance, if you look up “best smartphone for photography,” you will find phone models that are good for taking pictures, even if the page doesn’t use those exact words.
Semantic search uses tools like vector embeddings, and machine learning to give results that better match what people are really searching for. This results in better answers that understand the situation and greatly cuts down on irrelevant or poor-quality responses.
Enhances User Experience
We’ve all experienced that. You type a simple question into a search engine, but it doesn’t show you the answers you want. So you try to ask the question in a different way. And then a different way.
Nobody wants to search for the same thing five times to find the answers they need. Semantic search engines are good at giving you helpful results right away, which makes using them a pleasant experience.
Semantic search makes it easier for users by providing results that are more clever and helpful. It focuses on what the user really wants instead of just the words they type in. It helps people find information more quickly, even if their questions are unclear, or not well written.
For example, if someone asks, “Where did the last Olympics happen?” semantic search knows that “last Olympics” means a specific event and gives the right answer (like “Tokyo 2021”), even if those exact words aren’t used.
It also has features like asking questions by voice, suggesting words as you type, and answering questions, all of which need a good understanding of human language. Semantic search reduces frustration and makes it easier to use by providing search results that are relevant, personalized, and clear.
Increases Engagement and Conversions
Semantic search helps people find what they’re really looking for by connecting their needs with the best content or products. This leads to more interaction and sales. When users can quickly find what they’re looking for, like a blog post, a product, or a service, they’re more likely to engage, spend more time, and do something.
In online shopping, semantic search helps understand what customers are looking for, like when someone types “laptop for video editing.” It can show them the best laptops for that purpose, even if “video editing” isn’t a specific word used in the product description.
This lowers the number of people leaving the site quickly and makes it easier to find products. On content platforms, it helps readers find articles or videos that they like and need. This keeps them engaged for longer and makes them happier.
For businesses, this means more people are taking action, whether it’s buying something, signing up, or doing anything else they want them to do. So, semantic search connects what businesses provide with what users really want, increasing both relevance and profits.
Supports Voice Search
With the popularity of digital helpers like Siri, Alexa, and Google Assistant, using voice to search for things has become more common. Semantic search is important for helping with this change because it helps systems understand and respond to spoken language.
Voice searches are usually longer and sound more like a natural conversation. For instance, someone might ask, “What’s the weather like in Paris next weekend?” or “Can you suggest a good action movie from the 90s?”
Regular keyword searches have a hard time with these kinds of questions, but semantic search can grasp the purpose, and connections between ideas. It also helps keep the conversation clear in longer chats, making it easier and more natural for users to talk.
This is important not just for personal help apps, but also for customer service robots, online shopping helpers, and more. By helping machines to “understand” and talk like people, semantic search is essential for creating user experiences that feel natural and are focused on voice interaction.
Enables Context-Awareness and Personalization
Semantic search helps create a more personalized and relevant experience for users, which people now expect in their online interactions. Semantic search can give better results by understanding what people are asking and using information like their past searches, likes, location, and what device they’re using.
This makes the results more personal for each user. For example, if you search for “best restaurants” on your phone in the evening, you will see nearby places to eat dinner instead of general information about restaurants.
This tailored approach is more than just using keywords; it makes users feel noticed and cared for. In online shopping, this could mean suggesting items based on what you’ve looked at before or what’s popular right now.
In education or content platforms, it could mean organizing materials based on what a user has liked before or their skill level. Semantic search helps provide smart recommendations by understanding how data is connected and what it means.
This makes for a more straightforward and enjoyable experience. This personal touch encourages users to stay loyal, keeps them coming back, and strengthens the relationships between users and the platforms.
Semantic Search Examples
There are many ways to use semantic search, such as in search engines, online shopping sites, and business searches. Let us give you some examples of how semantic search provides better search results.
Google Search
Imagine you’re looking for a laptop charger. If you search for “laptop charger” using a regular search engine, it will show you pages with that exact phrase, but it won’t think about the bigger picture.
On the other hand, a search engine like Google can tell that you are in Nevada. And you have been looking into a 95w laptop charger. In that case, it would recommend good lists of the laptop charger and stores near you where you can buy them.
Google AI Overviews
Let’s say you’re looking for a laptop charger for a certain situation. If you type a long question in the Google search box, you’ll probably get a summary from an AI in the results.
This AI search result doesn’t just give you links; it gives you an answer to your question. The summary mentions certain products and their features and shows you useful resources.
Amazon Search
Imagine you are looking for a planner to help you plan your workday. If you type “best planner for work” in the Amazon search bar, the system will know you’re looking for things like time blocking, hourly schedules, and to-do lists. If you’ve already looked at or bought related products, the results will consider that as well.
Instacart Search
Imagine you want to buy some beverages, but you want to make sure they are mostly healthy. If you look for “healthy beverages” on Instacart, the search might not bring up things that have “healthy” in their description. Instead, it will recognize that you are looking for products that have features like low sodium or no artificial flavors.
Tips to Perform Semantic Search Optimization
Now that you understand how semantic search works and why it matters for your business and customers, you need to learn how to include it in your SEO plan. Here are our tested tips to use semantic SEO and make sure your content stays relevant in the future.
Choose Natural Language Instead of Keyword Stuffing
If you haven’t done it yet, stop cramming keywords into your content. This old method involves putting the same keywords too many times in website content, like in titles and meta descriptions.
It makes the website not fun for visitors. Since semantic search looks at topics instead of just keywords, this practice isn’t needed. Make content that feels like it was written by a person.
Use the way your audience talks, and write in a friendly, conversational style. Keep using important words in your writing. But don’t hesitate to use everyday language. For example, instead of saying “best laptop charger,” you can say “quick charging laptop charger”.
Use Semantically Relevant Keywords
Semantic search tries to grasp the overall subject of your page, rather than just focusing on the main keyword. To help search engines understand better, include related words called latent semantic indexing (LSI) terms.
For example, if you are writing about laptop chargers, you might want to use related words like:
- Types of chargers like 95w and 180w
- Charger qualities such as quick charging and light weight
- Brands like Dell and HP
Create Pillar Pages and Topic Clusters
Keywords are still important for making your content easier to find online. Just focusing on one keyword isn’t enough. Instead, you need to show your wide range of experience. Set up your website using pillar pages and topic clusters.
- Pillar pages are detailed pages that include everything important about a subject. It gives you all the basics to begin, but it doesn’t cover details on smaller topics.
- Topic clusters are groups of related content that explore a topic in detail. The pillar page usually connects to these pages, providing readers with a full range of information on a topic.
Make an Internal Linking Strategy
Internal links are useful for a few reasons. They help people visiting the website find more interesting information on topics they like. They also help create semantic relationships. This helps crawlers see how your content is related and how much you know about the topic.
Also Read: What Is Faceted Navigation and Why Does It Matter for Your Website SEO?
Understand and Talk to What the User Wants
To make your content rank better, you need to understand what your audience is looking for and why they want it. In other words, you need to figure out why they are searching. Are they looking for a basic guide on a subject?
A strong opinion about a trend in the industry? Or a detailed comparison between your product and your top five competitors? You don’t have to guess. SEO tools show what people want when they search for keywords, and they can be grouped into five main types.
Informational: The person wants to find out more about a subject or get an answer to a question.
Commercial: The user is looking at different choices while thinking about what to decide. Transactional: The user is prepared to do something specific, like buying a product. Navigational: The user is looking for a particular website or page.
Local: The user is looking for products or services nearby.
For example, when people look for “laptop chargers,” they want to find a store nearby (local) or compare different products (commercial). This matches the search results we pointed out earlier.
Use Structured Data
Structured data isn’t something that visitors can see on your website. Instead, it’s a framework for adding code to your website that helps crawlers understand its content better.
You can use schema markup for things like FAQs, how-to guides, reviews, videos, recipes, and other stuff. It can make search results show more detailed information. Even if it doesn’t create rich snippets, it still gives crawlers useful information about your content.
Leverage Social Media
To create a good semantic search plan, consider things outside of your website. Use YouTube and other social media to help provide searchers with the information they need. For example, your YouTube video could be one of the top results when people search for a particular term.
It can also show up in the “What people are saying” section, which includes comments from social media and discussion sites. You can also improve the video script, title, and description for this video to get better results.
To Conclude
Semantic search is the future of smart ways to find information. By figuring out what users really mean and the situation they’re in when they ask questions, it gets past the limits of basic keyword searches and makes online experiences feel more like talking to a person.
Using technologies like NLP, knowledge graphs, and vector embeddings, semantic search provides very relevant and personalized results that suit users’ needs based on their language, behavior, and context.
It can be used in many areas, like helping chatbots and virtual assistants, improving how people find products, and making customers happier in online shopping. As users want more natural conversations and accurate answers, semantic search helps keep them engaged, loyal, and ready to make purchases.
It doesn’t just make our searches better, it changes how we discover, understand, and interact with information. In a time where everything is fast, customized, and available worldwide, using semantic search is not just about improving technology. It’s essential for staying important and competitive in the market.
FAQs
How does semantic search make search results more relevant?
Semantic search makes results more useful by understanding the meaning behind words, not just matching them exactly. It knows similar words, the situation, and what the user wants, so it can find answers that use different words but mean the same thing. For instance, if you look for “affordable smartphones for taking pictures,” you might find information about low-cost camera phones, even if you didn’t use those exact words. This makes searching easier and more precise.
Can semantic search work with questions in different languages?
Yes, semantic search is getting better at understanding questions in different languages and between different languages. By concentrating on the main idea instead of the exact words, it can connect questions and information in different languages. Advanced models can create language-neutral representations, so a user’s question in Spanish can show relevant information written in English. This makes semantic search especially useful for worldwide platforms and users from different countries.
How does semantic search affect online shopping websites?
In online shopping, using semantic search makes it easier to find products, keeps customers happy, and boosts sales. When people look for something like “winter boots for hiking,” semantic search understands what they mean and shows them products made for tough winter conditions, even if those words aren’t in the product description. This makes it easier to find products, get better suggestions, and encourages people to buy more.
Is using semantic search difficult for businesses?
Setting up semantic search needs some technical skill and the right tools, but many new platforms and APIs make it easier. Services like Elasticsearch, Google Cloud Search, and OpenAI embeddings help businesses add smart search features without having to create everything themselves. Big companies might find it useful to create their own custom models and knowledge graphs. The difficulty can change, but the lasting benefits in how happy and involved users are usually make the effort worth it.
What does the future hold for semantic search?
The future of semantic search will involve more personalized results, a better understanding of context, and interactions that feel more like talking to a person. With improvements in AI, especially big language models, searching will be more like having a conversation. It will adapt better and remember what you talked about in multiple exchanges. Working with voice helpers, virtual and augmented reality, and smart devices will make semantic search a part of our daily lives, not just something we use on screens.